Files
Submission Date
Fall 2024
Abstract
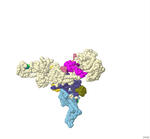
Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia (CPVT) is a potentially fatal condition linked to a mutation in the Ryanodine receptor (RyR2), the largest calcium ion channel known, which is crucial for heart function. The RyR2 protein is made of four similar subunits. Mutations in RyR2 can cause the channels to "leak," disrupting normal heart rhythms. In individuals with this mutation, the combination of caffeine intake and exercise can worsen these effects, leading to sudden cardiac arrest. With the RyR2 receptor located on the sarcoplasmic reticulum of cardiac muscle, the mutation prevents the receptor from fully closing, which hyperpolarizes the membrane and disrupts the ion flow required for healthy heart contractions. Despite extensive research on RyR2, the specific impacts of more than 250 mutations linked to cardiomyopathies remain largely unknown. A 3-D printed model was developed from the merged PDB-ids 7UA1 and 7UA3 to highlight the main characteristics of the RyR2 channel with calmodulin and a drug, ARM210 bound to the protein. ARM210 is important because it can effectively stabilize leaky channels by binding near the bound ATP and initiating a cascade of conformational changes influencing the channel to approach a closed state. A spacefill model (thickness 4.0) was printed due to the protein’s large size. Only one of the four subunits, 4,883 amino acids long, was printed in this model. The N terminus is colored blue, and the C terminus is colored red. Three domains are known to be mutation hot spots and are labeled in the model as: The N terminal domain (NTD) from amino acids 1-642 in gold, the central region from amino acids 2100-2500 is colored palevioletred. This is where the key mutation in this molecular story is found (R2474S and labeled cyan). The channel domain from amino acids 4486-4968 is labeled in skyblue. The central domain from amino acids 3613-4207 is labeled darkslateblue. Calmodulin is bound to the RYR2 protein and labeled fuchsia. Key amino acids that bind the calmodulin and stabilize it to the channel are Asp2473, Lys2563, and Gln21257, and are shown in purple. The ATP bound to the chain is shown in lime and the drug (ARM210 – KVR) is shown in teal. Ser 2312 and Glu2405 are amino acids found to be stabilizing the normal arginine at position 2472 which are shown in dark green. Amino acids that form the helix-loop-helix motif that interacts with the original arginine (Met 2406 and Arg 2418) are shown in black. Key amino acids involved in the xanthine (caffeine) binding site are colored orange and are Trp 4645, Tyr 4944, Glu 4194, and Tyr 4644. The calcium binding/passage site is shown in white and the amino acid that interacts with the calcium is Glu3922. The EF hand domain from amino acids 4016 – 4090, plays a role in regulating the gating of the calcium release channel and is colored olive.
Recommended Citation
Athwale, Harani Ritesh; Patel, Dillen-Preetesh Jayanti; and Kothuru, Sai Puneeth, "Modeling the Function of Ryanodine Receptor Type 2 and its Role in Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia (CPVT) Heart Disease" (2024). Protein Modeling Reports. 19.
https://nsuworks.nova.edu/protein_modeling_reports/19