Files
Submission Date
Fall 2024
Abstract
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, specifically through improper differentiation of young blood cells into healthy red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Some of the mutations involved in AML have been traced back to the Isocitrate Dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2) enzyme. IDH2 is an enzyme within the citric acid cycle that converts isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) with NADP+ being reduced to NADPH as an important cofactor. Mutations in IDH2, such as R140Q and R172K, cause the protein to convert α-KG to the oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate (2HG). These changes block the differentiation of blood cells, resulting in many young malformed cells in the blood, leading to AML.
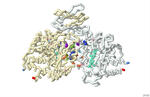
The binding of the drug AG-221 to mutant IDH2 enzyme at an allosteric binding site stabilizes the enzyme in an open, inactive conformation, and prevents the formation of 2HG. This alleviates symptoms of AML. However, most patients will need additional chemotherapy and often complete bone marrow transplants. A 3-D printed model was produced based on PDB-ID: 5I96 and 5I95 showing how AG-221, NADPH, and α-KG bind to the mutated IDH2 enzyme. Specific amino acids that interact with AG-221 at the binding site interface on the mutated IDH2 enzyme are highlighted in various colors in the model; Y311, D312, Q316, L320, I319, L298, L160, W164. The drug binds tightly and remains bound to the enzyme for an extended period to enhance therapeutic efficacy. The NADPH is shown to bind in the model of IDH2 enzyme, and it is highlighted in aquamarine. NADPH is shown because of its importance to the function of the protein as an electron acceptor.
Additionally, the R140Q mutation on the enzyme is highlighted in light cpk on the model to emphasize the change from arginine to glutamine. This change is important as the amino acid at position 140 becomes smaller and uncharged in the mutated form. The R172K mutation on the enzyme is highlighted in cpk colors. The model shows position 172 in the nonmutated form as arginine. The 3-D printed model also includes spacefill models of both α-KG and 2HG. By inhibiting the production of 2HG and reversing the block in cell differentiation, AG-221 helps to manage the progression of AML in patients with the IDH2 mutation and creates a targeted treatment approach to alleviate symptoms. Its use can cause the occurrence of cells with this mutation to be greatly reduced and make bone marrow transplants more effective.
The 3-D printed model also demonstrates the AG-221 drug binding within the binding interface of the two chains of the isocitrate dehydrogenase protein. The drug acts as an inhibitor for the α-KG substrate and the NADPH cofactor. The focus of this model is on the R140Q due to a personal connection to the mutation.
Recommended Citation
Balani, Bhumika; Matta, Jay; Punjal, Nitya; and Bourke, Brianna, "Modeling Isocitrate Dehydrogenase 2 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Exploring how the drug AG-221 Inhibits 2-hydroxyglutarate Production and Restores Blood Cell Differentiation" (2024). Protein Modeling Reports. 17.
https://nsuworks.nova.edu/protein_modeling_reports/17
IDH2-presentation
IDH2 poster.pdf (567 kB)
IDH2-poster
Dr. Melissa Dore Video Interview - Leukemia, Idhifa, IDH2 and bone marrow donations.docx (13 kB)
Interview wtih Dr. Melissa Dore Explaining Leukemia and Impact of Project